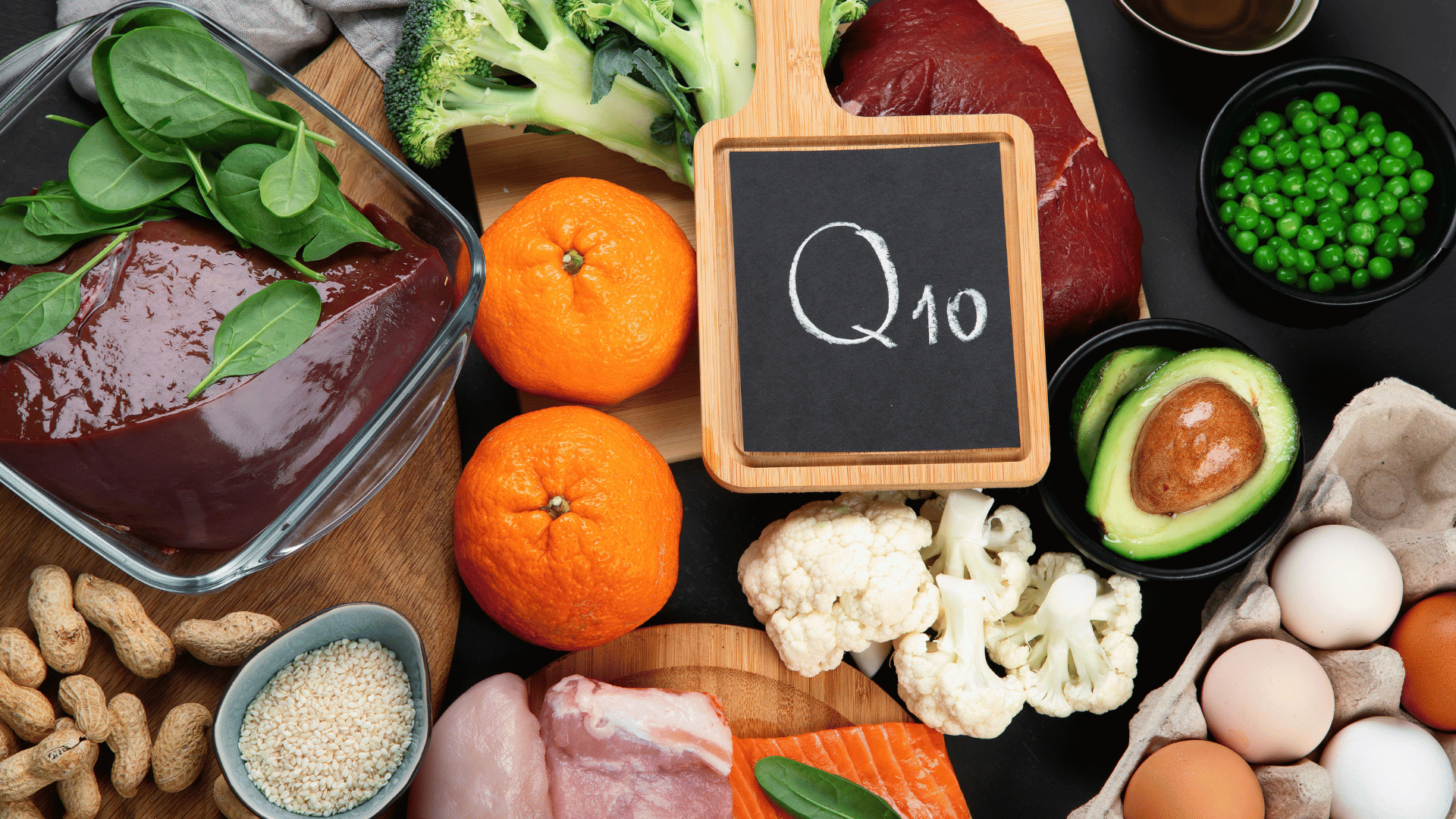about
Supplements
The treasure lies within food
When I was first diagnosed with cancer, I took the opportunity to ask the doctor during rounds which nutritional supplements were better. However, the doctor advised me to obtain nutrients from a variety of foods. With a balanced diet, most nutrients can be obtained. Later, I learned that single foods contain multiple nutrients. For example, although fish oil contains Omega-3 fatty acids (including EPA and DHA), eating more fish not only provides the nutrients in fish oil but also additional protein, iodine, selenium, calcium, iron, vitamin A, and D. Many people spend a lot of money on expensive ingredients or medicinal herbs but forget that the treasure is in food. However, some nutrients may indeed need to be supplemented, such as vitamin D, which many cancer patients commonly lack. In such cases, you can ask a doctor or medical center to perform a blood test to determine if additional purchase is necessary.
Miraculous Probiotics
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 contributes to inhibiting the growth of cancer cells, enhancing the immune system, and reducing the risk of cancer [Note 2] [Note 3]. Cancer patients are advised to daily intake 1000-2000 International Units (IU) of Vitamin D3 [Note 4]. To enhance the anti-cancer effect, the concentration of Vitamin D in the blood should be maintained at 30 ng/mL or above [Note 5]. Animal-based foods rich in Vitamin D3 include cod liver oil, fatty fish, egg yolks, and dairy products. Plant-based options comprise fortified plant-based dairy, orange juice, and cereals [Note 1].
Omega-3
EPA, found in Omega-3, is especially beneficial for individuals with cancer. Abundant sources of Omega-3 can be obtained from fish oil, particularly from deep-sea fish like salmon, mackerel, and cod [Note 1]. Generally, the recommended daily dosage of Omega-3 should be between 1 gram to 3 grams [Note 2]. To maintain an anti-cancer blood concentration, the ideal balance of Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA in the blood varies based on individual health conditions [Note 3]. Animal-based sources include deep-sea fish, while plant-based sources encompass flaxseed oil, nuts, and other plant oils [Note 4].
Q10
Q10 is beneficial for improving treatment effectiveness and alleviating side effects in cancer patients. The recommended daily intake for the general population is 30 to 200 milligrams of Coenzyme Q10. Animal-based foods containing Coenzyme Q10 include beef, pork, poultry, and fish. Plant-based foods include cauliflower, spinach, nuts, olive oil, etc. [Note 1].
High-Dose Vitamin C Injections
Apart from the potential risk of hemolysis in individuals with Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, a small number of people may experience low blood sugar after injection. For some cancer patients, high-dose vitamin C injections have shown significant efficacy with low side effects[Note 1].
https://www.eliteclinic.com.tw/tw/dr-liu-pojen/305-hdivc
Selenium
Selenium is considered beneficial for cancer patients due to its antioxidant properties, helping reduce oxidative stress and boosting immunity to combat inflammation and, consequently, cancer [Note 1][Note 4]. The recommended daily intake for the general population is 50 to 70 micrograms [Note 2]. Selenium can be obtained by consuming foods rich in selenium, including animal products such as turkey, fish, and beef, as well as plant-based foods like garlic, nuts, soy, and wheat germ [Note 2][Note 3].
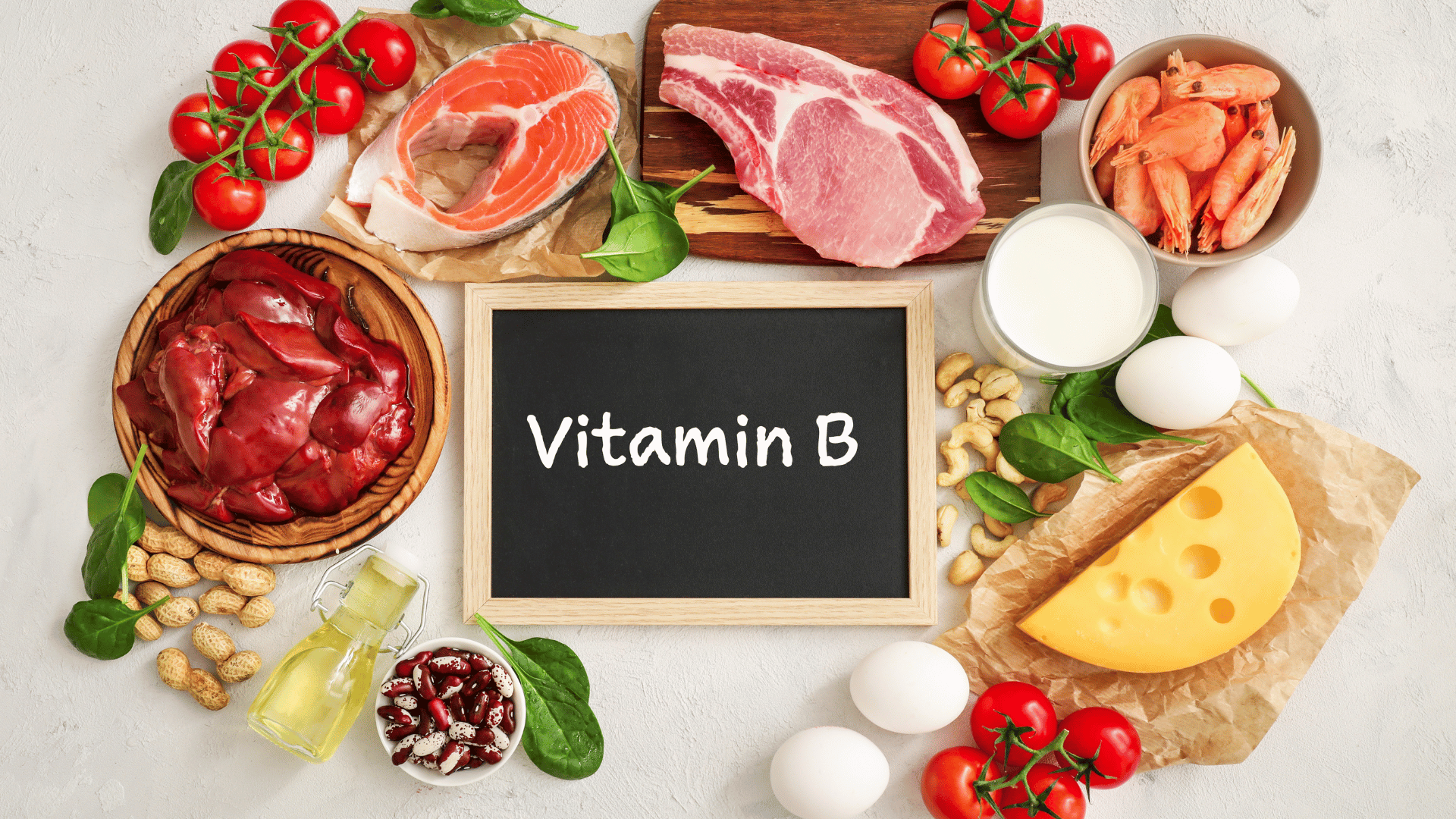
Vitamin B Complex
Before my first round of chemotherapy, the doctor directly gave me a bottle of vitamin B complex, stating that it could alleviate the side effects of chemotherapy. Experts point out that vitamin B complex also helps maintain the normal functioning of the nervous system and metabolism, enhances the body’s immune function, and contributes to reducing fatigue and increasing appetite [Note 3][Note 6]. The recommended daily intake varies for individuals based on age, gender, and physiological condition, and it is suggested to obtain it through a balanced diet [Note 2]. Currently, there is no specific blood concentration data to guide cancer treatment, but moderate intake of vitamin B complex is beneficial for overall health [Note 6]. People can obtain vitamin B complex by consuming animal products such as meat, dairy, and eggs, as well as plant-based foods like whole grains, nuts, legumes, and leafy green vegetables [Note 1][Note 5].